If you’ve ever wondered what computer parts can be recycled, the answer is almost all of them. Recycling computers matters for three big reasons: it protects the environment, it keeps your personal data safe, and it allows materials to be reused instead of wasted.
Think about this: according to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, recycling just one million laptops saves enough energy to power 3,500 homes in the United States for an entire year (EPA, 2025). That’s a massive impact from equipment that otherwise might sit in a closet or end up in a landfill.
The truth is, nearly every part of a computer—from the motherboard to the power supply—has recycling potential. Knowing what can be recycled helps you make smarter choices for both your home and business. That’s why choosing EACR Inc for computer recycling ensures your old devices are managed securely, sustainably, and with the environment in mind.
Benefits of Recycling Computer Components

Environmental protection
Computers contain hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium. When these end up in landfills, they can leak into soil and water. Recycling keeps toxins out of the environment and reduces the strain on natural resources.
Data security
Hard drives and SSDs store sensitive information. Responsible recycling ensures that data is properly wiped or physically destroyed so it can’t fall into the wrong hands.
Energy savings & material recovery
Computers are full of metals such as gold, silver, and copper. Recycling recovers these materials, reducing the need for energy-intensive mining.
| Internal Components | External Components |
| Motherboards & Circuit Boards: gold, silver, palladium, copper. | Computer Case: steel or ABS plastic (with flame retardants). |
| Computer Case: steel or ABS plastic (with flame retardants)CPU – gold, silicon, ceramics. | Monitors & Screens: CRTs (leaded glass), LCD/LEDs. |
| RAM Modules: gold connectors, IC chips | Keyboards & Mice: plastic, wiring, small circuit boards |
| Hard Drives: aluminum casing, rare earth magnets, platters | Peripherals: cables, webcams, speakers |
| Solid-State Drives (SSDs): chips with recoverable metals | Printers: motors, rollers, plastics, metal parts |
| Power Supply Units: copper wiring, aluminum, steel | Printer Cartridges: toner and ink cartridges |
| Graphics, Sound, and Network Cards: copper, gold, reusable components |
Internal Components That Can Be Recycled
Motherboards and Circuit Boards
Motherboards and circuit boards contain metals like gold, silver, palladium, and copper. Recycling facilities shred them to recover these materials, which are then used in manufacturing new electronics.
CPUs and RAM Modules
CPUs may be small, but they contain gold, silicon, and ceramics that are reusable when processed correctly. RAM modules also carry gold connectors and chips with trace amounts of metals, making them worth recycling.
Hard Drives and Solid-State Drives
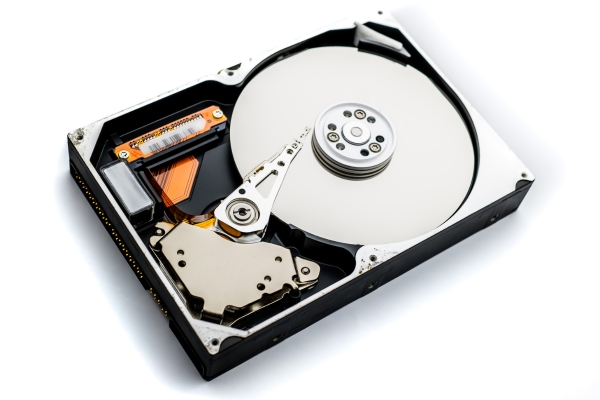

Traditional hard drives are built with aluminum casings, and magnetic platters. Solid-state drives contain chips with recoverable metals. Before recycling, both require secure data destruction to protect sensitive information.
Power Supplies
Power supply units contain copper wiring, aluminum, and steel—all recyclable materials. The cables attached to them can be stripped to reclaim copper and other reusable metals.
Graphics, Sound, and Network Cards
Expansion cards are smaller than motherboards but still carry reusable metals. They’re often refurbished for resale or broken down to extract copper, gold, and other recoverable components.
External Components That Can Be Recycled
Computer Case
The computer case is often made of steel, which is up to 90% recyclable, or ABS plastic. While steel is straightforward to recycle, plastic requires careful handling since it often contains flame retardants that can’t simply be landfilled.
Monitors and Screens
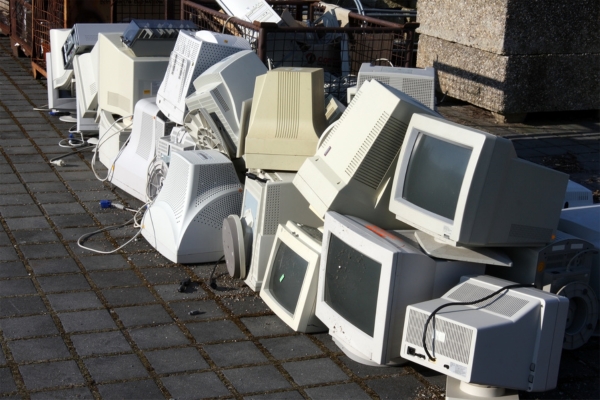

Older CRT monitors contain heavy leaded glass that must be processed separately. Modern LCD and LED screens, while lighter, and safer, must be properly recycled using trusted methods. Both types can be recycled, but they need specialized facilities to do it safely.
Keyboards, Mice, and Peripherals
These accessories are mostly plastic with small circuit boards and wiring inside. Once separated, they’re easy to recycle and prevent unnecessary plastic waste. Even the cords can be stripped to recover copper.
Printers and Accessories
Printers and similar accessories contain motors, plastic parts, metal rollers, and circuit boards. Toner and ink cartridges can often be refilled or recycled on their own, keeping them out of landfills while reducing plastic production.
Hazardous Materials That Need Special Handling
Not everything in a computer can go straight into the recycling stream. Certain parts require extra care:
- Batteries (CMOS, lithium-ion): Toxic and flammable if mishandled. They must be processed by specialists.
- Flame retardants in plastics: Common in cases and cables, and they can’t safely be dumped in landfills.
- Mercury in older displays and switches: Highly toxic, requiring isolation and proper disposal.
Reuse vs. Recycling: What’s the Difference?
When deciding what to do with old computers, it’s important to know the difference:
- Reuse: If the computer or parts still work, they can be donated, resold, or repurposed. RAM, cables, and even hard drives (after wiping data) can often find a second life.
- Recycling: When reuse isn’t an option, components are broken down into raw materials like steel, copper, and plastic.
Reusing comes first because it saves the most energy and resources. Recycling is the fallback when reuse isn’t possible.
What Happens After Recycling?
The recycling process for computers is more detailed than most people realize:
- De-manufacturing: Trained workers strip out parts like boards, drives, and power supplies.
- Shredding & separation: Conveyor belts and magnets sort steel, copper, plastics, and other materials.
- Smelting & refining: Precious metals are extracted from shredded boards and chips.
- End products: These recovered materials are used to make new electronics.
Conclusion: Why Responsible Computer Recycling Matters
Recycling computers isn’t just about clearing space—it’s about protecting the environment, safeguarding your data, and recovering materials that keep our technology cycle running.
By recycling responsibly, you prevent toxic substances from entering landfills, help conserve natural resources, and stay compliant with regulations.

